How to improve the nitrogen and phosphorus removal effect in low temperature environment?
Lowering temperatures often cause sewage plants to face severe challenges, especially the growth of activated sludge and the effects of nitrogen and phosphorus removal.
Within a certain temperature range, every time the incoming water temperature decreases by 10°C, the microbial activity will double. When the water temperature is lower than 4°C, the microorganisms will almost stop their life activities, and the sewage treatment effect will decrease or even disappear completely. Therefore, in order to balance the adverse effects of low temperature, it is necessary to control the operating parameters in advance before the water temperature changes significantly to adapt to the needs of environmental changes.
1. What impact does low temperature have on sewage plants?
01 Low temperature will weaken nitrification and denitrification
The viable environmental temperature for nitrifying bacteria is between 4-45°C, the optimal temperature for nitrosifying bacteria is 35°C, and the optimal temperature for nitrifying bacteria is 35-42°C.
Below the optimum temperature, the activity of nitrifying bacteria also decreases as the temperature decreases. When the temperature drops by 10°C, the maximum specific proliferation rate and activity of nitrifying bacteria are reduced by at least half. At 12°C, the reaction rate drops by 50%. At 5°C, Stop nitrification.
The optimal temperature for denitrification is between 15-20°C. Below this temperature, the metabolic capacity of denitrifying bacteria drops to a low level, and the denitrification reaction is significantly inhibited. When the temperature is lower than 5°C, denitrification almost stops. .
02 Low temperature will indirectly affect the biological phosphorus removal effect
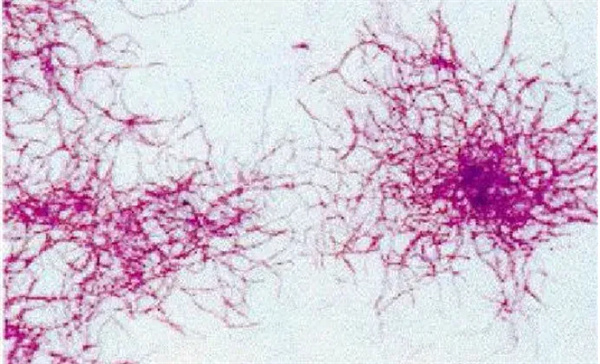
Phosphate-accumulating bacteria are cold-tolerant bacteria. Usually, the temperature drop during normal operation should have little effect on it, but the effect will be significantly reduced during actual operation.
There are three main aspects of the impact on biological phosphorus removal in low-temperature environments: lowering temperature affects the metabolism and physiological activity of microorganisms, and the proliferation rate of microorganisms decreases, thereby affecting the phosphorus release and phosphorus absorption effects of phosphorus-accumulating bacteria, resulting in systematic phosphorus removal Decreased functionality.
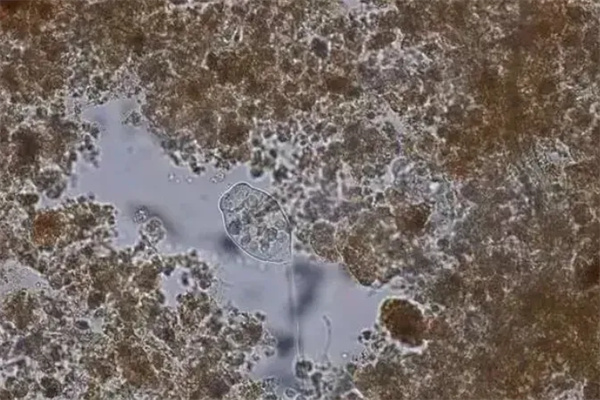
Phosphorus-accumulating bacteria under the microscope
Under low temperature conditions, polysaccharomyces bacteria become the dominant bacterial group in the biochemical system, and the dominant position of phosphorus-accumulating bacteria is destroyed. For the new nitrogen and phosphorus removal process coupled with activated sludge and biofilm, under low temperature conditions, the total phosphorus removal rate is more obviously affected by organic load than normal temperature.
03 Low temperature may cause sludge expansion
When the temperature is low, the growth of normal active bacterial flora in sewage is inhibited and reproduction is slow. Among them, microorganisms of the genus Microthrix that are suitable for low-temperature growth will multiply and grow in large numbers at suitable temperatures.
These bacteria will connect with each other and aggregate into groups during the growth process, thereby forming larger particles and producing a large amount of residual sludge. If not removed in time, it will cause sludge expansion in the sewage treatment plant.
04Low temperature reduces sludge settling performance
After the temperature decreases, the activity of the microbial flora in activated sludge decreases, the secretion of extracellular polymers on the cell surface decreases, and the interaction between microorganisms decreases, making it difficult to combine to form lumpy polymers.
This will cause the activated sludge particles to be finely broken and difficult to form large-particle flocs, thereby reducing the settling performance of the sludge particles and reducing the mud-water separation effect. As a result, fine suspended particles often appear in the effluent, which affects the effluent effect.
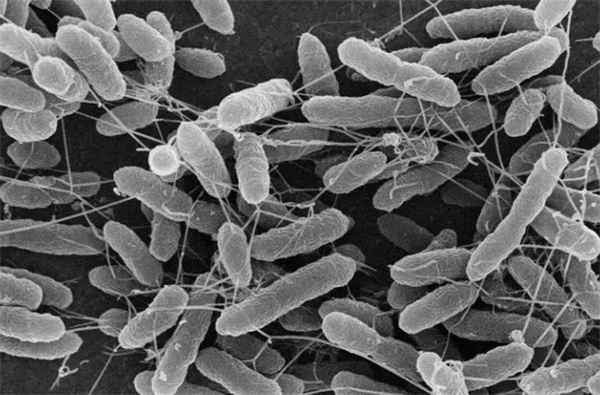
05 Low temperature reduces sludge activity
Low temperature will seriously affect the metabolism of microorganisms, resulting in a decrease in sludge activity. It is mainly reflected in the following three aspects: at low temperatures, the activity of microbial surface proteins in activated sludge decreases, and the fluidity of the protoplasmic membrane on its surface decreases, which is not conducive to the transportation of nutrients by microorganisms.
Activated sludge under the microscope
Lower temperature also inhibits the activity of enzymes in microorganisms, hinders the utilization of nutrients by microorganisms, and prevents microorganisms from absorbing nutrients normally, thus inhibiting the growth of microorganisms, causing the number of microbial flora in activated sludge to decrease and the activity to increase. to reduce. During the process of nitrogen and phosphorus removal, the activity of nitrifying bacteria, phosphorus accumulating bacteria and other microorganisms will also be affected by temperature, and the growth rate will decrease, resulting in an increase in the age of the sludge, resulting in the loss of these active microorganisms.
06 Low temperature will affect the solubility of nutrients required by microorganisms
Low temperature usually reduces the solubility of organic substances in water. However, different organic substances have different solubilities in water, and their solubility changes with temperature changes are also different.
The lower water temperature causes changes in the solubility of nutrients required for the growth of various microorganisms in activated sludge, which may cause changes in the ratio of different nutritional components, which may deviate from the optimal ratio required for microbial growth, which is not conducive to the growth of microorganisms. metabolic processes.
Microorganisms under the microscope
Lower water temperature overall reduces the content of nutrient sources required for the growth of microorganisms in the water. Compared with higher water temperatures, more nutrients may need to be added to ensure the normal growth of microorganisms in activated sludge, which increases the wastewater The operating cost of the treatment plant; a large amount of organic matter that should be used as an energy source cannot be dissolved in the water and used by microorganisms, which may also lead to the production of a large amount of sludge, affecting the concentration of activated sludge.
2. Low temperature may cause sludge expansion
01 Human intervention as early as possible to improve the adaptability of microorganisms to low temperature
Generally speaking, microorganisms will gradually adapt to the temperature of the surrounding environment during the process of growth and metabolism, but this adaptation process usually takes a long time.
At present, the seasonal transition in most cities is not obvious, and the arrival of autumn and winter is often accompanied by a sudden drop in ambient temperature. In this case, it is difficult for microorganisms to easily adapt in the short term, and humans need to supplement microorganisms that are more adapted to the environment.
Therefore, sewage treatment plants should summarize the temperature changes in previous years and make corresponding plans in advance. When the temperature begins to drop in autumn, slowly replace activated sludge to steadily improve the adaptability of microorganisms to low-temperature weather.
02 Pay attention to the nutrient content of sewage and adjust the proportion of organic components
The activity of microorganisms in activated sludge is greatly affected by the ambient temperature. The normal growth of microorganisms will be greatly inhibited at low temperatures. In order to maintain the growth, proliferation and metabolism of microorganisms under low temperature conditions, sewage treatment plants need to pay close attention to the content of various nutritional components in the sewage and appropriately adjust the proportion of organic components according to the actual situation.
For example, sewage treatment plants can supplement carbon sources or adjust the proportion of nutrient components such as carbon sources and nitrogen sources. This can provide sufficient nutrients and appropriate nutrients for the growth of microorganisms to ensure the normal growth of microorganisms, so that the activated sludge can still maintain sufficient vitality under low temperature conditions in autumn and winter to maintain the effective operation of the sewage treatment plant.
03 Ensure stable sludge discharge and control sludge age
Experienced operation and maintenance personnel must know that the microbial activity in activated sludge is low in autumn and winter, so most of them will choose to increase the sludge concentration to maintain activity.
Sludge after discharge
But this approach often comes with some risks. Stably operating activated sludge contains a large number of microorganisms. If the sludge concentration is increased in a short period of time by no desludge or less desludge, the growth time of microorganisms will be too long, which will cause excessive aging of the sludge, leading to the occurrence of Biological foam or sludge expansion.
Therefore, regardless of any working condition adjustment, the stable discharge of remaining sludge must be ensured. Sewage treatment plants should adopt some moderate measures to control the age of sludge on the premise of ensuring stable discharge of sludge, which requires a long process adjustment process.
Source: Wastewater Treatment Learning