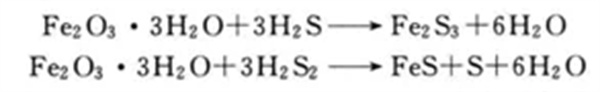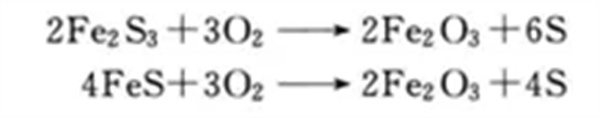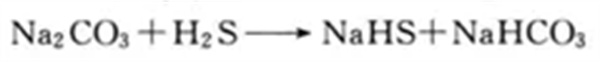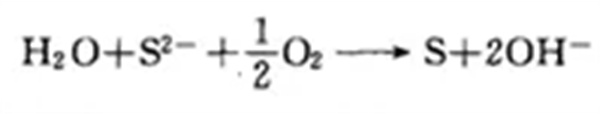Introduction to biogas desulfurization process
As an emerging energy source, biogas is used more and more widely. my country's environmental protection standards strictly stipulate that when using biogas energy, the H2S content in the biogas gas shall not exceed 20mg/m³. Whether in industrial or domestic gases, H2S must be removed as much as possible.
When biogas is produced from anaerobic fermentation equipment, especially during medium or high temperature fermentation, it carries a large amount of H2S. Since there is still a large amount of water vapor in the biogas, the water and the H2S in the biogas work together to accelerate the corrosion and blockage of metal pipes, valves and flow meters. In addition, the SO2 generated after the combustion of H2S combines with the water vapor in the combustion products to form sulfurous acid, which causes corrosion on the metal surface of the equipment, pollutes the atmospheric environment, and affects human health. Therefore, H2S must be removed from biogas before use.
Commonly used biogas desulfurization methods in the industry include: dry desulfurization, wet desulfurization, biological desulfurization and other desulfurization methods.
1. Dry desulfurization
Dry desulfurization is a simple, efficient and relatively low-cost desulfurization method, which is suitable for desulfurization of biogas with small biogas volume and low hydrogen sulfide concentration. Normal pressure iron oxide method is generally used for desulfurization, that is, a filler is placed in a container. The filler layer includes activated carbon, iron oxide, etc., with a thickness of 0.3~0.8m. The gas passes through the filler layer in the container from one end to contact with it at a rate of 0.4~0.6m/min. In 2 to 3 minutes, hydrogen sulfide is oxidized into sulfur or sulfur oxides, which remain in the packing layer, and the purified gas is discharged from the other end of the container.
During regeneration, take out the desulfurizer containing iron sulfide, sprinkle it with water, and expose it to air to oxidize it, then it can be reused.
2. Wet desulfurization
The wet desulfurization system mainly consists of two parts: absorption tower and regeneration tower. A sodium carbonate solution with a concentration between 2% and 3% is sprayed downward from the top of the absorption tower. At the same time, the biogas forms counter-current contact with the solution from bottom to top. In this process, hydrogen sulfide is effectively removed. After the sodium carbonate solution absorbs hydrogen sulfide, it will be transported to the regeneration tower. Under the action of the catalyst, the sulfur in the solution is decomposed, so that the sodium carbonate solution can be regenerated and recycled.
In addition, the effluent from the treatment plant can also be used to spray the biogas to remove hydrogen sulfide. When the temperature is 20°C and the pressure is standard atmospheric pressure, 2.3m³ of hydrogen sulfide can be dissolved per 1m³ of water.
3. Biological Desulfurization
The biological desulfurization process consists of three parts: a scrubber, a bioreactor, and precipitation and dehydration. The core link lies in the domestication and cultivation process of sulfur-eating bacteria. The principle of biological desulfurization is to use colorless bacteria to oxidize and convert sulfide into elemental sulfur. The chemical reaction formula is as follows:
The elemental sulfur generated through this reaction will contain a small amount of impurities, and these impurity-containing sulfur can be used in the sulfuric acid industry. During the combustion of sulfur to produce sulfuric acid, small amounts of residual biomass are automatically removed.
Another advantage of biological desulfurization is that the effluent from the treatment plant can be used to absorb hydrogen sulfide for biogas, and the absorption liquid can be treated together with organic wastewater containing high concentrations of COD, thus saving the cost of COD treatment. However, for now, the practical application of biological desulfurization technology in my country is still relatively limited.
4. Summary
In biogas treatment, if the hydrogen sulfide content in the biogas is high and the gas volume is large, the wet desulfurization method is more suitable. This method can not only remove hydrogen sulfide, but also remove part of the carbon dioxide, thereby increasing the proportion of methane in the biogas. If the site area is limited, dry desulfurization can be selected, but the desulfurizer usually needs to be replaced every three months. When biogas is used as fuel for gas engines, etc., in order to prevent problems with the operation of biogas nozzles or gas engines, the biogas needs to be deeply purified and filtered to remove solid particles in the gas. Filtration devices include gravel filters, gas filters, etc. Biological desulfurization is not widely used in China at this stage, mainly because its investment cost is relatively high.
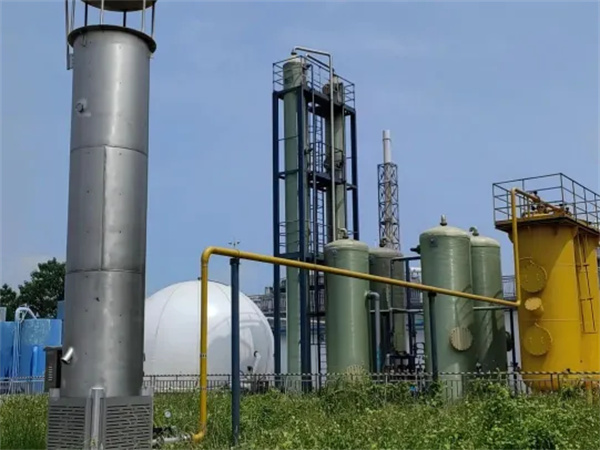
Live shots of biogas desulfurization at a pesticide production company in Jiangxi
The picture above is a real shot of the biogas desulfurization site of a pesticide manufacturer in Jiangxi. Our company is responsible for the design and construction of wastewater treatment and supporting biogas treatment. The biogas generated by the anaerobic reactor of this project is temporarily stored in a double membrane gas cabinet after being sealed with water, and then pressurized by a fan before entering the desulfurization system. The desulfurization system is equipped with wet desulfurization + fine desulfurization. The wet desulfurization can achieve the treated biogas H₂S≤ 200ppm, precision desulfurization as a backup unit can reach biogas containing H₂S≤50ppm. The desulfurized biogas can be utilized, or if not utilized, it can be burned and emitted through a biogas burner.
The desulfurization tower uses alkali liquid as the desulfurization agent. The alkali liquid absorbs hydrogen sulfide in the biogas and forms a rich liquid. The rich liquid is oxidized and regenerated in the regeneration tank to obtain alkali liquid and elemental sulfur. The regenerated alkali liquid is temporarily stored in the lean liquid tank, and then transported to the desulfurization tower through a pump to realize recycling of the alkali liquid. The elemental sulfur generated in the regeneration tank is discharged into the sulfur foam tank, dehydrated by the plate and frame, and then transported out regularly for treatment.
If you have needs for biogas treatment and resource utilization, please call the phone number on the card below for consultation.
Source: Internet