Introduction to wastewater treatment from polyformaldehyde production
Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal resin, polyoxymethylene, and polyacetal, is a thermoplastic crystalline polymer, known as "super steel" or "race steel".
As an engineering plastic with excellent performance, polyoxymethylene is widely used in many fields. In the automobile industry, polyoxymethylene is widely used in the manufacture of automobile parts, such as door handles, seat adjustment devices, fuel system components, etc. Because of its good wear resistance and mechanical strength, it can maintain its performance in complex use environments. Stable performance. In the field of electronics and electrical appliances, polyoxymethylene is often used to manufacture precision parts, such as small gears, switch components, etc. Its excellent electrical insulation and dimensional stability meet the demand for high-precision parts in electronic products. In addition, in industries such as machinery manufacturing and daily consumer goods, polyoxymethylene also occupies an important position due to its excellent comprehensive performance.
1. Polyformaldehyde production process
There are two major types of polyformaldehyde production processes, namely homopolymerization process and copolymerization process. Homopolyformaldehyde is a homopolymer of trimerformaldehyde, and copolymerformaldehyde is a copolymer of trimerformaldehyde and dioxane.
1. Homopolymerization process
The homopolymerization process is represented by DuPont in the United States. Pure formaldehyde is passed into an inert solution containing a cationic catalyst to polymerize into homopolymerization. The polymerization is operated semi-continuously. The polymer material is filtered and separated. After drying, it is hydroxyesterified with acetic anhydride. After capping, heat-stable polyformaldehyde is obtained, and then additives such as antioxidants are added, and the finished product is obtained through extrusion and granulation.
Homopolymer materials have good ductility and fatigue resistance, but are not easy to process and have a narrow processing temperature range. Homopolyoxymethylene is inferior to copolymer acetal in terms of thermal decomposition, thermal deterioration characteristics, hot water resistance, thermal stability, and acid and alkali corrosion resistance during molding. However, homopolymer has a higher degree of crystallinity, and its performance is slightly better than that of copolymer in terms of mechanical properties (strength, elastic modulus) and load deformation temperature that characterizes physical heat resistance.
Due to the complex formaldehyde purification process and technical difficulties in post-processing and end-capping of this process route, the homopolymer product has poor alkali resistance and heat resistance, and the production cost is high. Due to technical and economic problems, in recent years, only DuPont and Asahi Kasei Corporation have continued to use this process technology.
2. Copolymerization process
The copolymerization process is mainly bulk polymerization. Pure parformaldehyde, dioxane and boron trifluoride ether complex are mixed in a certain proportion, and then placed in a continuous kneader or twin-screw reaction with strong shearing and mixing effects. In the vessel, after the polymerization reaction is completed and post-processed, granular copolymerized formaldehyde is obtained.
The processing and molding conditions of copolymer acetal are not as harsh as those of homopolymer acetal, and less formaldehyde gas is released by thermal decomposition during the processing. All the indicators of the modified copolymer exceed those of homopolymer, and copolymer will become the future development direction.
China has been researching and producing polyformaldehyde for a long time. The trimer formaldehyde process technology is relatively reliable, but the polymerization process is backward. Since the end of the last century, foreign process technology has been introduced. In terms of technology sources, there are three main sources of technology for Chinese manufacturers, namely Polish ZAT technology. , Hong Kong Fuyi and South Korea's P&ID are all world-class technologies. At present, Poland's ZAT technology has stopped being sold, and only Hong Kong Fuyi and South Korea's P&ID are transferring their process technology to Chinese companies.
To sum up, the copolymer products produced by the copolymerization process have good thermal stability, aging resistance, hot water resistance, alkali resistance, oil resistance, chemical stability and easy processing, and their mechanical properties after filling with glass fiber It has been enhanced. In view of the advantages of its product quality being better than that of homopolymer, the growth rate of copolymer product output in the world is significantly higher than that of homopolymer product output.
2. Source of polyformaldehyde wastewater
1. Residues from the reaction process
In the polymerization reaction of polyoxymethylene, whether it is homopolymerization or copolymerization, it is difficult to achieve complete conversion of the monomers. Unreacted formaldehyde or trimerdehyde will remain in the reaction system. With subsequent separation, washing and other operations, these residual monomers are discharged with the water flow and become one of the sources of wastewater pollutants. Moreover, part of the catalyst used in the polymerization reaction may enter the wastewater with the flow of materials.
2. Washing and separation process
After the product is produced, it needs to be washed to remove impurities and unreacted monomers. A large amount of washing water will carry polyoxymethylene oligomers, residual monomers, and some additives added during the production process. During the separation process, some chemicals used for separation may also be mixed into the wastewater, increasing the complexity and pollution of the wastewater.
3. Equipment cleaning link
After long-term operation of polyoxymethylene production equipment, polyoxymethylene polymers and scaling will adhere to the inner walls of the equipment. During the equipment cleaning process, these substances will be washed down into the cleaning wastewater. Equipment cleaning wastewater usually contains high concentrations of polyformaldehyde and related impurities and is an important component of production wastewater.
3. Characteristics of polyformaldehyde wastewater
1. High chemical oxygen demand (COD)
Polyformaldehyde production wastewater contains a large amount of organic matter, including unreacted formaldehyde, parformaldehyde, and polyformaldehyde oligomers during the production process. These organic matter cause the COD value of the wastewater to be extremely high, and some can even reach tens of thousands of mg/L. A high COD value means that the wastewater contains high levels of organic matter and requires powerful treatment processes to reduce its pollution level.
2. Big difference in biodegradability
Different organic components in wastewater have different biodegradability. Small molecular organic compounds such as formaldehyde can be utilized by microorganisms under certain conditions and have good biodegradability. However, macromolecular substances such as polyformaldehyde oligomers have complex structures, which are difficult for microorganisms to decompose on them and have poor biodegradability. This requires the treatment process to consider how to improve the overall biodegradability of wastewater in order to better utilize biological treatment methods.
3. Contains toxic and harmful substances
Some chemicals or catalysts used in the production process may contain toxic and harmful substances. If these substances exist in wastewater, they will inhibit or even poison the microorganisms in the biological treatment system, affecting the effectiveness of wastewater treatment. At the same time, if these toxic and harmful substances are discharged into the environment without proper treatment, they will cause long-term harm to the ecosystem.
4. Polyformaldehyde wastewater treatment process
The main focus of polyformaldehyde wastewater treatment is pretreatment, because the removal of formaldehyde and COD is crucial for subsequent treatment. The high toxicity of formaldehyde will seriously inhibit the activity of microorganisms during biological treatment. If not removed in advance, it will lead to inefficiency or even failure of subsequent biological treatment links. A high COD value means that the organic matter content in the wastewater is extremely high. If it directly enters the subsequent treatment process, the treatment system will be overloaded and it will be difficult to ensure the treatment effect. Therefore, effective pretreatment is the key to ensuring the smooth progress of the entire wastewater treatment process.
1. Physical preprocessing
Precipitation: Gravity is used to precipitate suspended particles and some dense polyformaldehyde oligomers in wastewater to the bottom of the water. For some small particles that are difficult to naturally precipitate, flocculants (such as polyaluminum chloride, polyacrylamide, etc.) can be added to promote the particles to agglomerate into larger flocs and accelerate the precipitation process. The precipitation method can effectively remove some solid impurities in wastewater, reduce the adhesion carriers of formaldehyde and other organic matter, reduce the COD of wastewater, and reduce the load of subsequent treatment processes.
Filtration: Use sand filtration, activated carbon filtration and other filtration methods. Sand filtration can remove residual fine particles in wastewater, while activated carbon filtration uses the porous structure of activated carbon to adsorb some dissolved formaldehyde and other organic matter in wastewater, further reducing COD, improving the clarity and quality of wastewater, and creating favorable conditions for subsequent treatment. .
2. Chemical pretreatment
Oxidation treatment: Common oxidation methods include Fenton oxidation, ozone oxidation, etc. Fenton oxidation uses the reaction of ferrous ions and hydrogen peroxide to produce strong oxidizing hydroxyl radicals. The hydroxyl radicals can attack formaldehyde and other organic matter in wastewater, oxidize and decompose them into small molecular substances, and reduce formaldehyde concentration and COD. Ozone oxidation uses the oxidizing property of ozone to directly react with organic matter and formaldehyde, destroying their chemical bonds and causing their degradation, effectively reducing formaldehyde content and COD value.
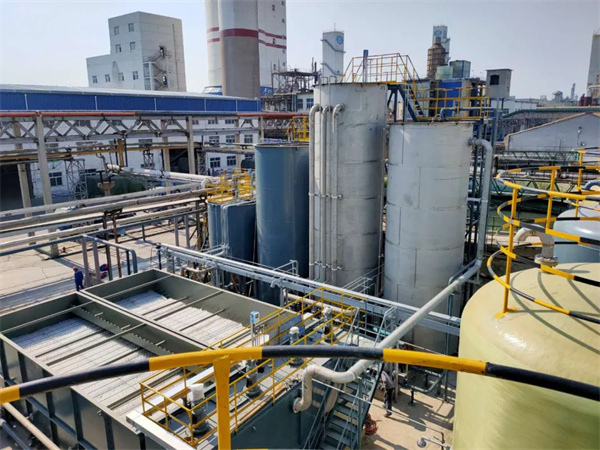
The production wastewater pretreatment unit in the 40,000 tons/year high-end modified polyformaldehyde project of Yankuang Lunan Chemical Co., Ltd. uses the Fenton fluidized bed reactor independently developed by our company (Patent No. ZL201420213094.6). This reactor adopts fluidized bed technology based on the original Fenton reaction tank, which keeps the catalytic packing inside the reactor to a greater extent, while making the catalytic oxidation reaction proceed more thoroughly, resulting in better effluent quality and reducing the amount of chemicals. The amount of sludge added and produced.
The design water volume of this project is 60m³/h, the inlet water COD ≤ 5000mg/L, formaldehyde ≤ 500mg, the outlet water index is COD ≤ 500mg/L, formaldehyde ≤ 20mg/L. It has been running stably for 4 years.
Neutralization reaction: Depending on the pH of the wastewater, neutralization treatment may be required. If the wastewater is acidic or alkaline, adjust the pH value of the wastewater to a range suitable for subsequent treatment by adding acid-base regulators (such as lime, sulfuric acid, etc.). Appropriate pH values help improve the efficiency of pretreatment processes such as oxidation reactions, better remove formaldehyde and reduce COD, while avoiding adverse effects on treatment equipment.
3. Follow-up processing
Biological treatment: Pretreated wastewater can be treated by biological treatment processes such as activated sludge method or biofilm method. In the activated sludge method, the activated sludge microorganisms in the aeration tank feed on the remaining organic matter in the wastewater and convert it into carbon dioxide, water and the cell material of the microorganisms themselves through metabolism. The biofilm method uses microorganisms in the biofilm attached to the filler to decompose organic matter. These biological treatment methods can further remove biodegradable organic matter in wastewater and reduce COD content.
Advanced treatment: In order to meet more stringent emission standards or achieve wastewater reuse, advanced treatment is also required. For example, reverse osmosis technology is used to allow water molecules to pass through a semipermeable membrane under pressure and intercept salt and other small organic molecules. The ion exchange method can be used to remove specific ions in wastewater, further improving the quality of wastewater, so that the treated wastewater can be discharged up to standard or reused, achieving the dual purposes of rational utilization of water resources and environmental protection.
Through the above series of treatment methods, polyformaldehyde production wastewater can be effectively treated to meet environmental protection requirements while achieving rational utilization of resources. If you have polyformaldehyde wastewater treatment needs, please call the phone number below for consultation.
Source: Internet